
How to Choose the Right Car Radiator
The radiator is typically located at the front of the engine compartment behind the vehicle's grille, where cool air can pass through the radiator, removing heat from the coolant inside. Parts of a Radiator A typical radiator has an inlet tank, an outlet tank, and a center core comprised of tubes encased in fins.

84614525 General Motors Radiator Shutter Assembly. Lower, MOUNTING, LITER Island GM, Duncan BC
The thermostat has a valve worked by a chamber filled with wax. When the engine warms up, the wax melts, expands and pushes the valve open, allowing coolant to flow through the radiator. When the engine stops and cools, the valve closes again. Water expands when it freezes, and if the water in an engine freezes it can burst the block or radiator.
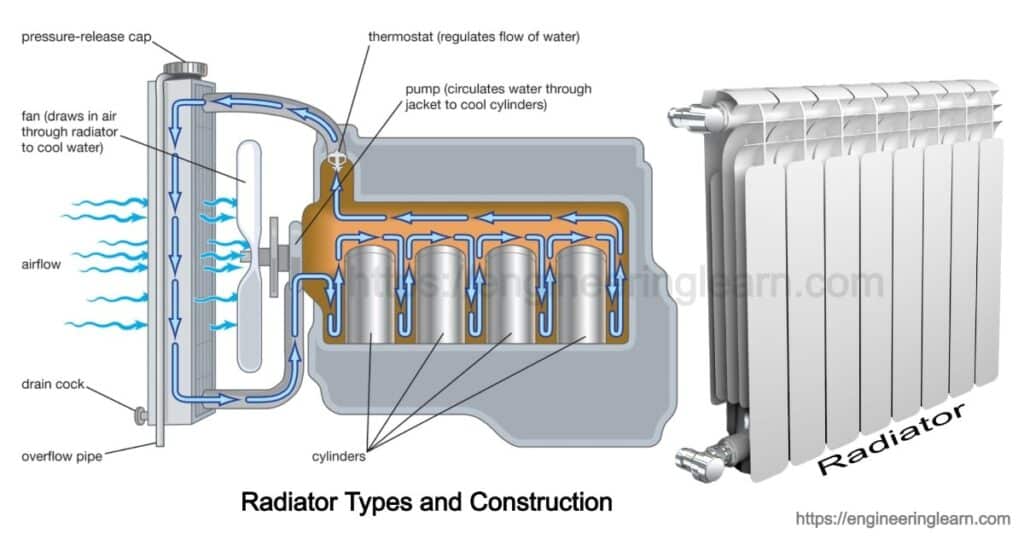
Radiator Types and Construction Engineering Learner
The coolant flows from the inlet to the outlet through many tubes mounted in a parallel arrangement. The fins conduct the heat from the tubes and transfer it to the air flowing through the radiator. The tubes sometimes have a type of fin inserted into them called a turbulator, which increases the turbulence of the fluid flowing through the tubes.
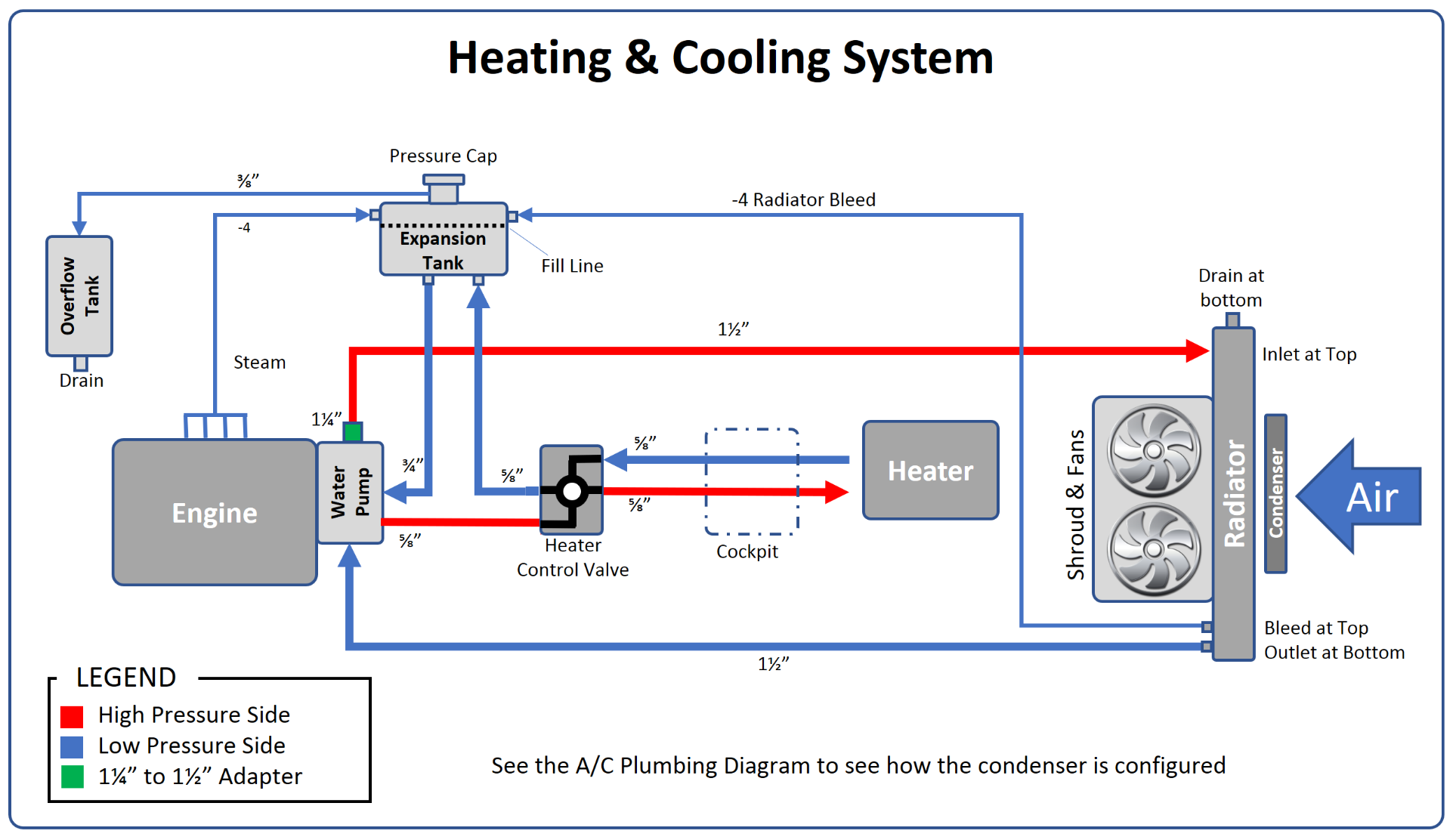
Radiator — Swartz Garage
The basic parts of a radiator consist of two tanks with a set of tubes connected with thin fins that radiate heat away from the tubes. As air passes through the fins, the heat is carried away, lowering the temperature of the fluid running through the tubes. Modern vehicles use aluminum radiators, most with plastic side tanks, but there are also.

Car radiator and cooling systemAutodesk Online Gallery
The overflow tank holds coolant. When the level in the cooling system gets too low, coolant is withdrawn from the storage to enter the cooling system. On the other hand, if there's too much pressure, coolant will be pulled from the cooling system back into the overflow tank. Because the cooling system is a closed unit, the amount of coolant.

Car Radiator Car, Radiator Car Radiator, Car Buying, Radiators, Graphics, Radiant Heaters
Radiator. The radiator is one of the most important components of a modern cooling system as it has the task of cooling down the high-temperature water that makes its way out of the engine. It is made up of three parts - an upper tank, a lower tank, and a core. The water first arrives in the upper tank or inlet tank and makes its way.
Removing the Radiator I Have a the Car Listed Above It Is a Turbo...
Watch the animated video on how the engine cooling system in an automobile works.
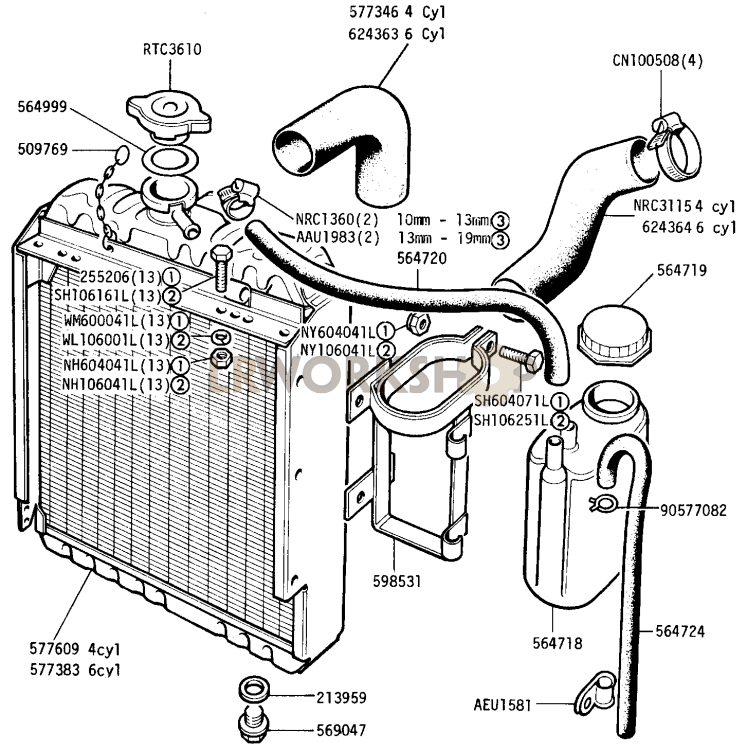
Car radiator diagram information gmpbcdallas
Radiators are classified according to the direction of the water flow through them. In some, the water flows from top to bottom-down flow type radiator. In other, the water flows horizontally from an input tank on one side to another tank on the other side-cross flow type radiator. Radiators are usually made of copper and brass because of their.

2 Schematic of Radiator Assembly. Download Scientific Diagram
Automobile - Cooling, Radiator, Engine: Almost all automobiles employ liquid cooling systems for their engines. A typical automotive cooling system comprises (1) a series of channels cast into the engine block and cylinder head, surrounding the combustion chambers with circulating water or other coolant to carry away excessive heat, (2) a radiator, consisting of many small tubes equipped with.

Northern Radiator® 205215 Muscle Car Radiator
interconnecting hoses to transfer the coolant from engine to radiator (and also to the car's heater system where hot coolant is used to warm up the vehicle's interior). to turn the AC on. If the fan begins to work, suspect the temperature sensor in the fan circuit (you will need a wiring diagram for your vehicle to find it). In order to.
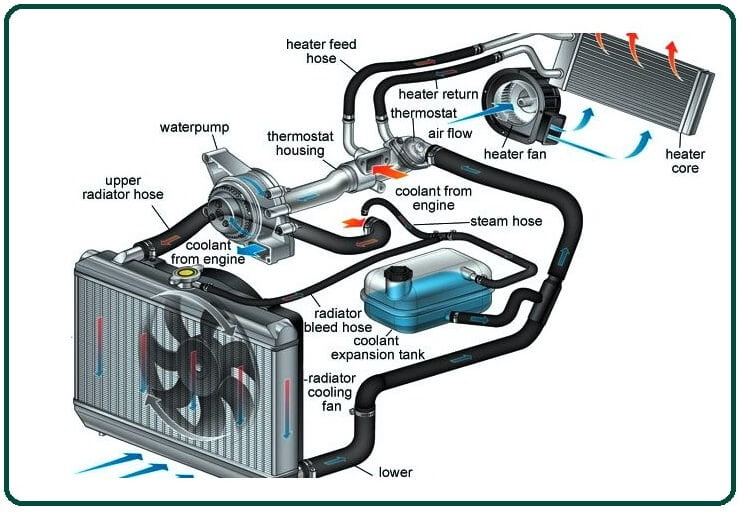
How Does a Radiator Work? Parts of Radiator Coolant In The Radiator
When the clutch input speed is 3000 rad/min and the temperature is 100 °C, the output torque is 19.04 N·m, the speed is 2877.2 rad/min, and the slip rate is 4.3%. Due to the shape memory effect.

Radiator and Components
How do radiators work? How a radiator works and how a radiator helps in the process of cooling your engine. The entire engine cooling process is explained.Pl.

Car radiator and cooling systemAutodesk Online Gallery
Most of the energy in the gasoline (perhaps 70%) is converted into heat, and it is the job of the cooling system to take care of that heat. In fact, the cooling system on a car driving down the freeway dissipates enough heat to heat two average-sized houses! The primary job of the cooling system is to keep the engine from overheating by.
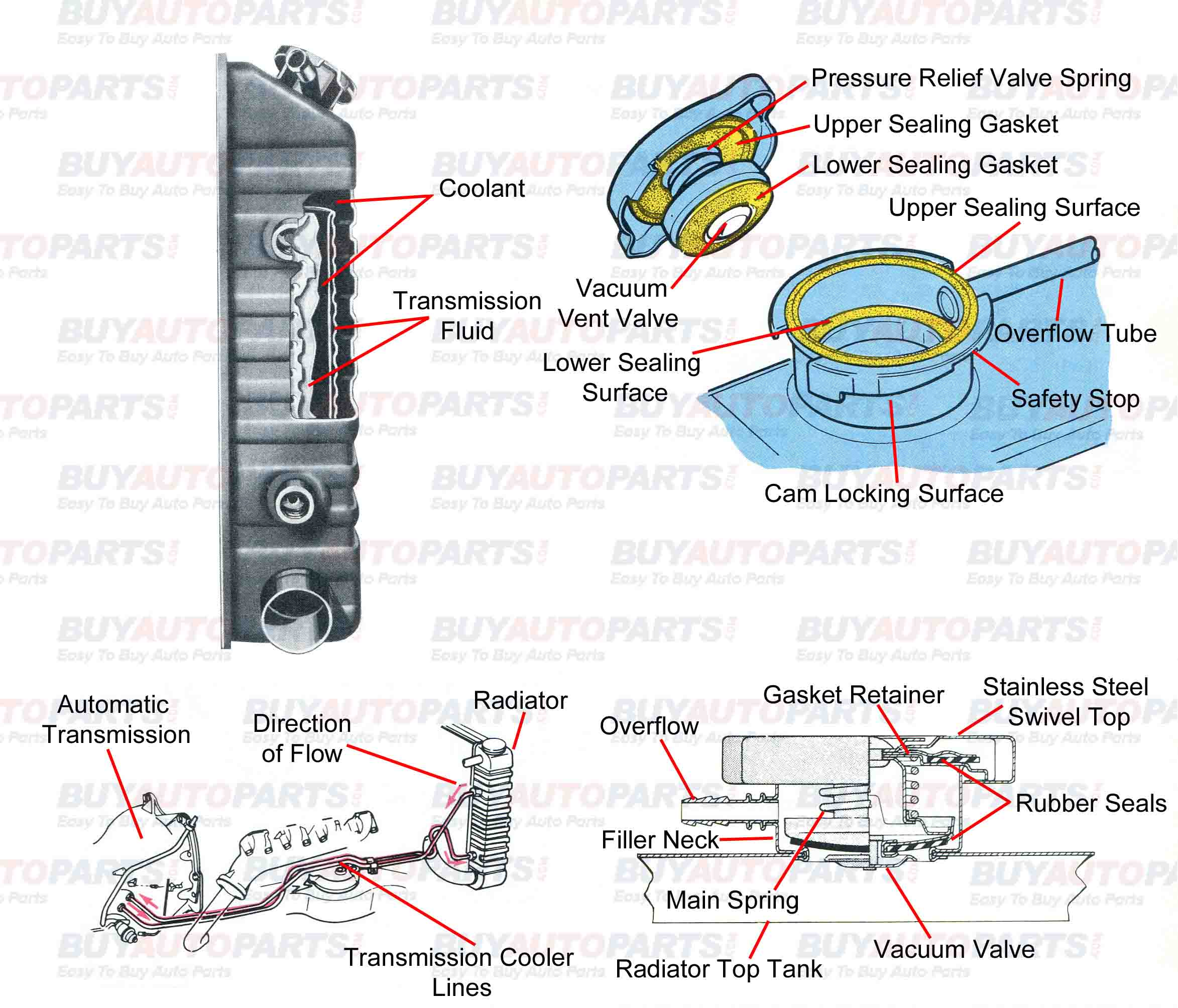
Car Radiator Diagram Buy Auto Parts
Remove the radiator cap for either way. Once the cap is removed, you can either open the petcock valve or remove the bottom radiator hose to drain the coolant. Drain the coolant into a plastic reservoir. 4. Disconnect the Radiator. With the coolant drained, you can start removing hoses, clamps and the radiator bolts keeping the radiator in place.

Car Radiator Explainedakqky.pdf.pdf DocDroid
Flushing and Filling is Easy as 1-2-3! Remember to flush and fill your radiator every 24 months or 24,000 miles. Drain your cooling system. Flush with water and a quality flush product. Fill with 50%-50% or 70%-30% antifreeze water mixture. Use more antifreeze if you drive in extreme temperatures.

Northern Radiator® 205027 Muscle Car Radiator
Like your radiator at home, a car radiator contains a network of pipes running from the so-called top tank to the bottom tank. Unlike your radiator at home, though, the one in a car is a dense mass of thin aluminium layers in a honeycomb structure that surrounds the pipes carrying the coolant. The heat passes from the coolant to the aluminium.